
Generative AI (GenAI), isn’t just a buzzword anymore.
It’s not a fad that can be swept under the rug or read about and put away—it is a genuinely transformational technology advancement that forward-thinking businesses are leveraging to their benefit.
According to a study by MIT Sloan, many of the surveyed business leaders indicated that they intended to become more proficient in AI and believed it would help their businesses gain or maintain a competitive edge. Similarly, a study by PWC revealed that 55% of respondents reported their companies had invested in AI, ranking it as a top-3 investment priority above any other listed technology.
Given the utility afforded by recent advances in mainstream generative AI, and the number of generative AI companies developing solutions, businesses are beginning to recognize GenAI’s benefits and implement it within their processes.
However, between business leaders hoping to gain a competitive edge and companies prioritizing AI above any other listed technology-these three questions come to mind when we stop to consider companies who want to add generative AI into their workflows:
- What type of generative AI should your business invest in?
- Does your business have a clear generative AI strategy?
- How will generative AI integrate with your existing systems and workflows?
If your business has already addressed these questions and is implementing generative AI – you’re ahead of the curve. But if your business is still figuring out where to start, you should delve deeper into understanding the potential of generative AI and how it fits within your company.
What is generative AI?
In simple terms, generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence that employs deep learning models to create content. GenAI content can range from images and text to videos and code, all produced based on a model’s training. GenAI pushes the boundaries of AI’s role from analytical to creative, allowing users to create original content and create unique solutions.
Unlike traditional AI models that focus on analysis and interpretation, generative AI’s core functionality revolves around the ability to produce and innovate. Generative AI is not about understanding or processing data but creating new data.
Unlike discriminative models that predict inputs, classify data points, and learn using probability estimates, generative models can generate new examples. Generative models go in-depth to show the actual data distribution and learn the different data points, rather than model just the decision boundary between classes.
How generative AI works
Training a generative model involves feeding it a large amount of data so that the model can learn the distribution and structure of that data. Once trained, the model can generate new data points with similar statistical properties.
However, training these generative models is computationally intensive and requires a lot of data.
Fortunately, improvements in hardware, data storage, and model architecture have significantly mitigated these challenges. Enhanced processing power from GPUs and TPUs, scalable cloud storage solutions, and optimized neural network designs have collectively enabled the efficient training of large-scale generative models.
These advancements have made developing and deploying sophisticated generative AI systems feasible, paving the way for their widespread application across various industries.
Generative AI examples
As more generative AI applications hit the market, businesses must identify the best use case for GenAI. Knowing the available types of GenAI is the first step in leveraging this technology effectively.
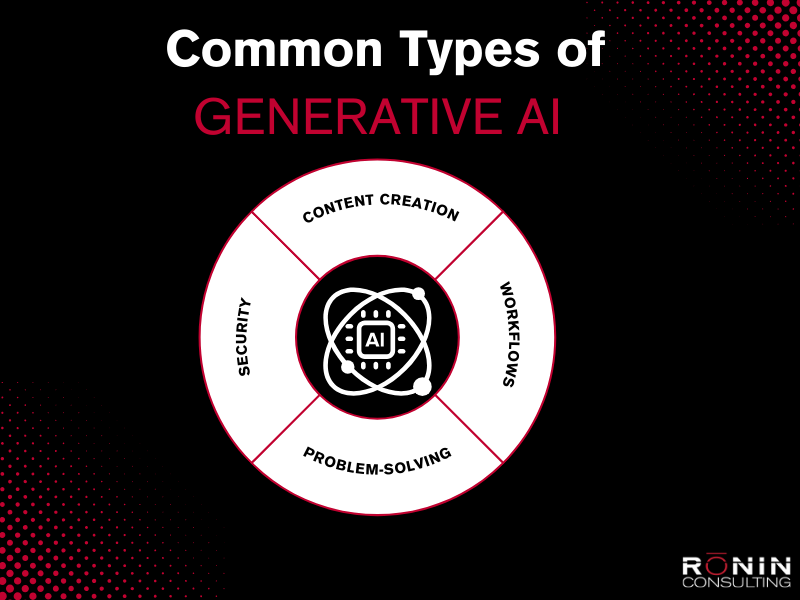
Some of the most common uses of GenAI today are:
- Content creation
- Workflow enhancement
- Problem-solving
- Security
Content creation
Content creation is essential for engaging audiences and delivering valuable information across various platforms. By leveraging GenAI, businesses can enhance their creative processes and streamline many content deliverables. Examples of content creation include:
Text generation: Generative AI platforms like ChatGPT, or Microsoft Copilot can create articles, blog posts, and reports, aiding in content marketing and documentation.
Image and video generation: Tools like GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) can produce realistic images and generative AI videos that are useful for entertainment, advertising, and virtual reality experiences.
Music and audio composition: AI can compose original music, create soundscapes, and generate voiceovers. This is perfect for businesses who want to create compelling videos or get into podcasting.
Workflow enhancement
Improving workflow efficiency and accuracy is crucial to staying competitive. Using AI-powered tools that can help streamline various aspects of workflow, like enhancing productivity and minimizing errors, is a game changer for many businesses today.
Automated code generation: Writing and debugging code accelerates software development processes and reduces human error.
Data analysis and visualization: Generative models can create data-driven insights and visual representations, aiding in decision-making and strategic planning.
Simulation and modeling: Simulating complex systems and processes is helpful in various fields, such as manufacturing, logistics, and engineering.
Problem-solving
GenAI can be pivotal in addressing complex challenges across various domains, enabling innovative solutions and informed decision-making. Organizations that leverage AI can enhance their problem-solving capabilities and drive progress in their respective fields.
Innovation and design: Generating new product designs, architectural plans, and innovative solutions using gen AI fosters creativity in product development and design industries.
Financial modeling: Complex financial models and scenarios are straightforward for GenAI models to computer, and their outputs can aid investment strategies, risk assessment, and economic forecasting.
Security
AI significantly strengthens security by proactively identifying and mitigating risks, ensuring robust protection across various sectors. By integrating AI, organizations can enhance their ability to detect threats and maintain rigorous security standards.
Threat detection and prevention: GenAI models can analyze patterns in data to identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities, enhancing cybersecurity measures.
Fraud detection: Generative models can detect unusual patterns and behaviors indicative of fraudulent activity, providing early warnings and preventing financial losses.
Automated security protocols: Businesses can develop and enforce security protocols using AI, ensuring consistent application of best practices and reducing the risk of human error in security management.
While the above are not the only examples of GenAI, they are more common GenAI use cases that may benefit your business. Off-the-shelf solutions exist for these areas, but may not provide the specific functionality or a consistent user experience to fit into your existing software systems and workflow processes.
A custom solution that precisely meets a business’s unique needs and objectives while maximizing employee adoption will be a better option for many organizations.
Does your business have a clear GenAI strategy?
A clear generative AI strategy is crucial for successful implementation and maximizing the return on investment. With the market becoming inundated with new GenAI tools and apps, having a plan for your purchase will be essential to keep you on track and budget. Here are key components to consider when developing your plan:
Define objectives and use cases
Start by identifying specific business problems or opportunities where generative AI can add value. Do you want to use GenAI to summarize documents, or do you want to use it to help your team optimize workflows – or both? Clearly define the objectives you hope to achieve with this new technology so you have a vivid picture going into the process.
Assess readiness and internal capabilities
If needed, ask AI consultants to help. If you have a capable internal team, make sure they understand the data, hardware, software, security considerations, and technical expertise required to implement and maintain generative AI solutions.
Develop a roadmap
Create a detailed implementation roadmap that outlines the steps, timelines, and resources required for deploying generative AI. Include milestones for all projects, including full-scale implementation and continuous evaluation.
Understand privacy implications
Some off-the-shelf generative AI applications do not provide the level of privacy that you expect. Understanding the difference between public and private AI and selecting the appropriate GenAI solution for your business needs is crucial. For businesses with strict privacy regulations, prioritizing data safety, security, and confidentiality is essential.
Don’t get sticker shock
The off-the-shelf generative AI solution might be cheaper on the front end but can incur high data storage and usage costs, especially as your needs scale. Your best choice could be to invest in a custom built GenAI solution. Sourcing a custom solution might seem expensive upfront, but it can be more cost-effective in the long run.
Take your time and make the right generative AI choice
Our best suggestion is to plan, prepare, and study all options before choosing. Your AI strategy must weigh all of your options so you can make an informed decision. By taking a strategic approach, you can maximize the benefits of generative AI while minimizing potential risks and costs.
How will generative AI integrate with your existing systems and workflows?
Don’t assume that just because another business or friend you know is using an AI tool, your business can, too. Integrating generative AI with existing systems and workflows requires careful planning and coordination. It’s more complex than purchasing your solution and pressing play. You need to integrate it into your existing system and workflow, often requiring expert integration help.
Here are some steps to facilitate smooth integration:
Conduct a workflow analysis
Map out your current workflows to identify areas where generative AI can seamlessly integrate. Look for repetitive manual tasks, bottlenecks, and opportunities for AI automation.
Data integration
For AI systems to be very effective, they need access to high-quality data. Establishing robust data pipelines, ensuring data integrity, and restructuring your data storage solutions are crucial steps. This ensures that the AI can process and analyze the data accurately, leading to more reliable outcomes and insights.
Interoperability
Select a generative AI solution compatible with your existing software and platforms. This compatibility minimizes integration challenges and ensures a smoother transition. If you encounter difficulties, consider engaging with a consulting firm specializing in both AI and system integrations, like Rōnin Consulting, to provide expert guidance and support.
Training and change management
Once you have picked your AI solution and rolled it out, provide training for employees to ensure they are comfortable using new AI tools. Change management strategies can help smooth the transition to AI-enhanced workflows, address any resistance, and foster a culture of innovation.
Continuous monitoring and improvement
After integration, continuously monitor the performance of generative AI systems and their impact on workflows. Collect feedback from users to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the AI tools meet business objectives.
Integrate and invest with ease
Following these steps ensures that your generative AI integrates into your existing systems and workflows and maximizes its potential to drive change in your business. Careful planning, expert support, and ongoing refinement are key to unlocking AI’s transformative power.

When you’re ready to invest in generative AI
When you’re ready to invest in generative AI, addressing the fundamental questions can make your transition smoother and more effective. Integrating generative AI into your business strategy is not just a forward-thinking move but a necessary one to stay competitive. As evidenced by MIT Sloan and PNC studies, many business leaders recognize AI’s transformative potential and have begun to prioritize AI investments.
But, before making any big waves in generative AI remember to…
Confirm the type of generative AI your business should invest in. Evaluate your business needs and identify areas where generative AI can add value, such as content creation, workflow enhancement, problem-solving, or security. Understanding the different types of generative AI applications can help you choose the one that aligns best with your objectives.
Ensure your business has a clear generative AI strategy. Define your objectives and use cases. Assess your readiness and internal capabilities, develop a detailed implementation roadmap, and understand the privacy implications. This strategic approach ensures that your investment is aligned with your business goals and regulatory requirements.
Understand how generative AI will integrate with your existing systems and workflows. Conduct a workflow analysis to identify areas for AI integration. Ensure data integration, select compatible solutions, and provide employee training before rolling out your new system. Also, ensure you employ continuous monitoring, so you are always ready to refine your solution and maximize the benefits of generative AI.






If you want to explore adding GenAI to your business, reach out for a free, no-strings consultation call with us. At Rōnin, we have an AI platform called SamurAI™ that enables organizations to quickly implement solutions, securely utilize multiple AI models, and simplify integrations with existing business systems.